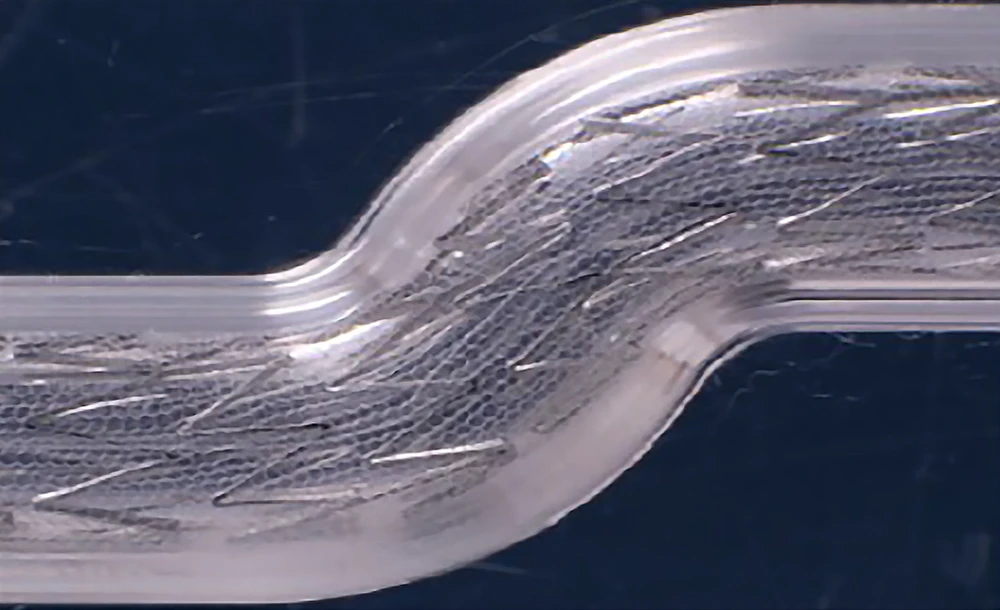
Explore the layers of carotid stent innovation
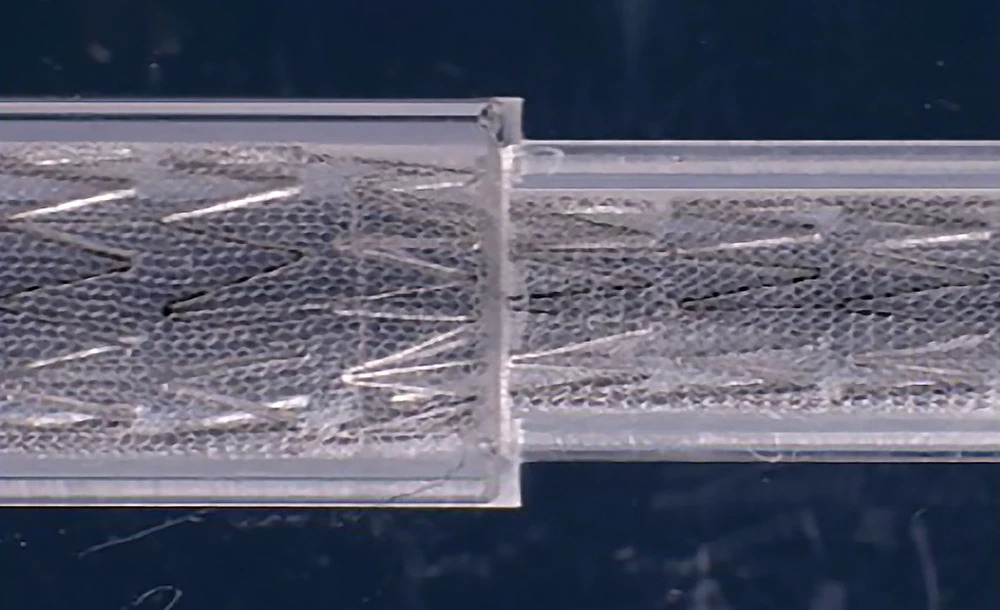
MicroNet Mesh-Covered Protection
- Made from polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a non-metallic material, to enhance endothelialization and lower the risk of thrombosis
- Closed-cell protection against plaque protrusion with the smallest mesh pore size (~150 – 180 μm)*
- Defense demonstrated beyond 5 years1**
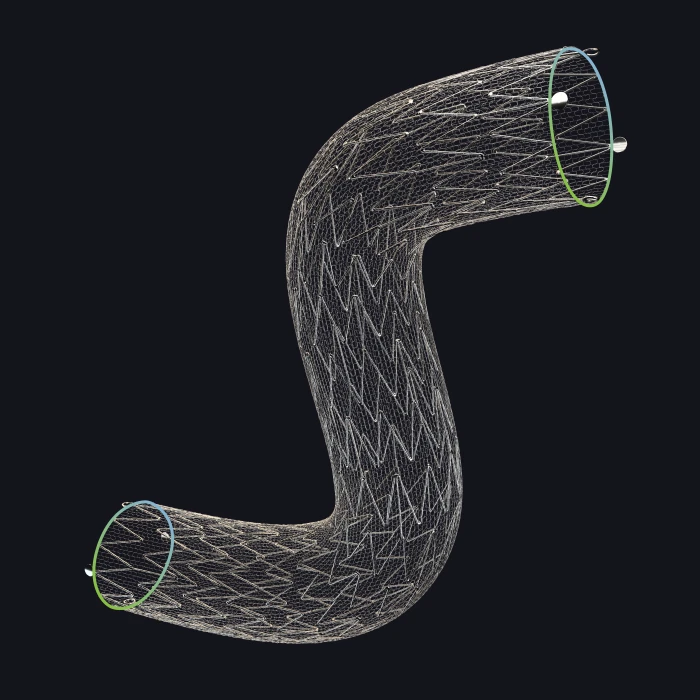
SmartFit Technology
- Self-expanding nitinol stent
- The largest open-cell frame* that allows for flexibility even in challenging or complex anatomies
- Supports accurate vessel wall apposition without the need for tapered configurations4
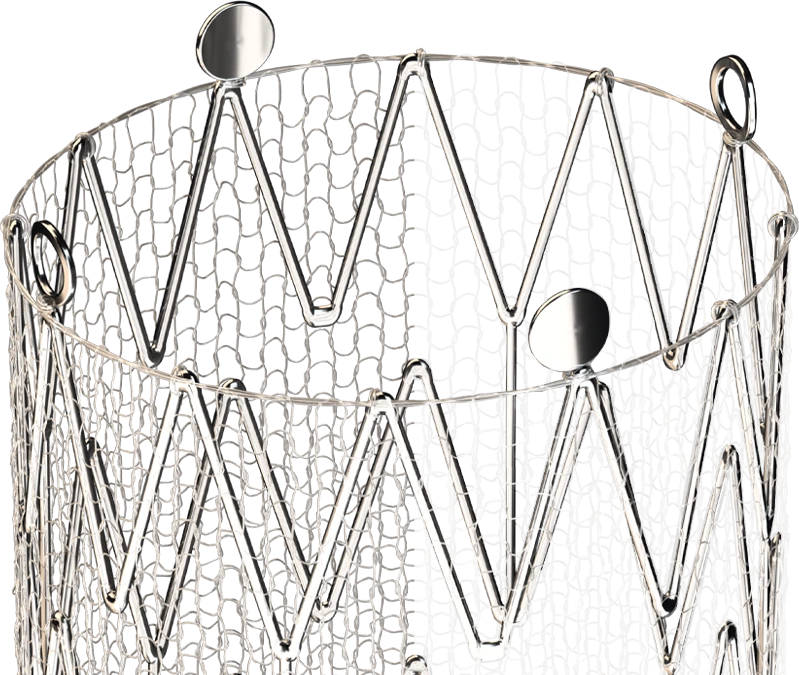

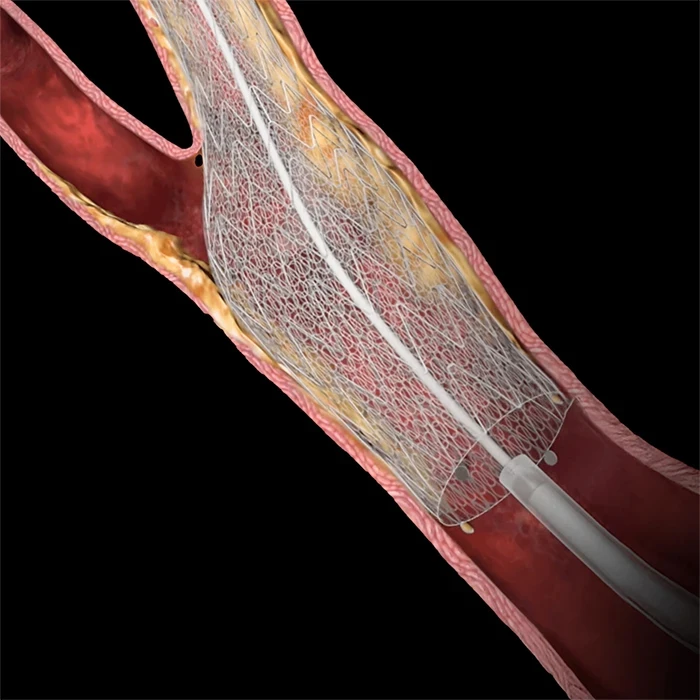
Evidence-based stroke prevention
CGuard Prime demonstrated the lowest 30-day and 1-year primary endpoint major adverse event rates of any pivotal study of carotid stenting (CAS) 2-11
(InspireMD)
MicroNet™ Mesh-Cover
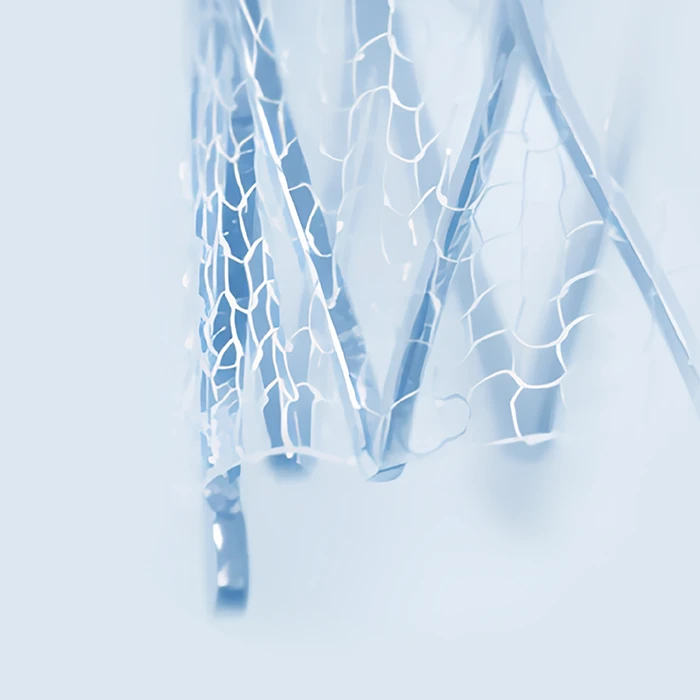

- Woven from a single 20μm strand of polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
- Chosen for biostability and non-thrombogenicity
- Provides optimal pore size to prevent embolization (average 165μm)
Provides lasting protection against restenosis, reducing the need for reintervention2
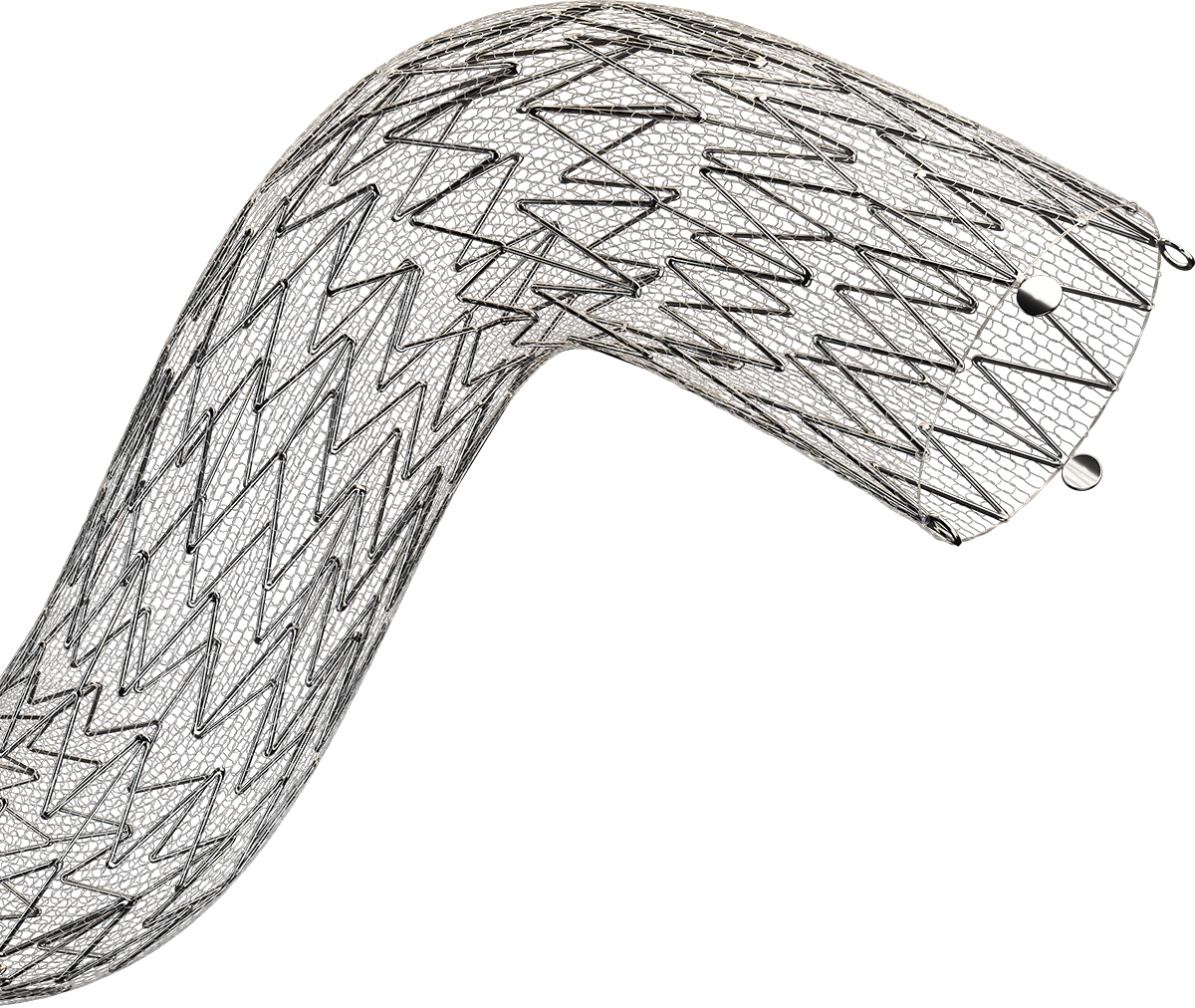

Designed to defend in a broad range of anatomies
Flexible
Nitinol frame design on a large open-stent cell platform
Accurate
Minimal foreshortening during placement and predictable coverage upon deployment
Conformable
Encourages natural vessel wall apposition after deployment, mitigating restenosis and reducing thrombus formation
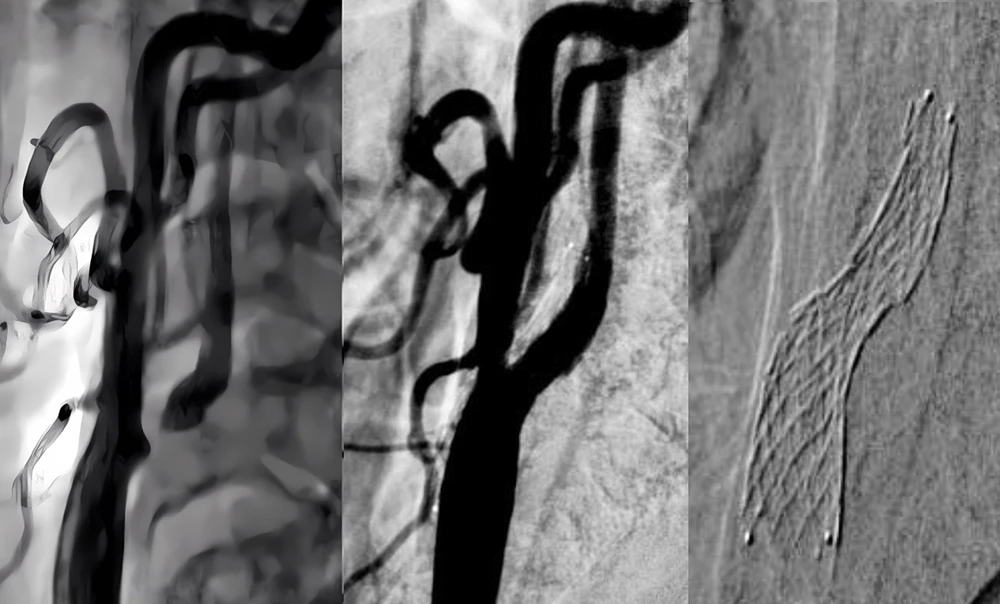
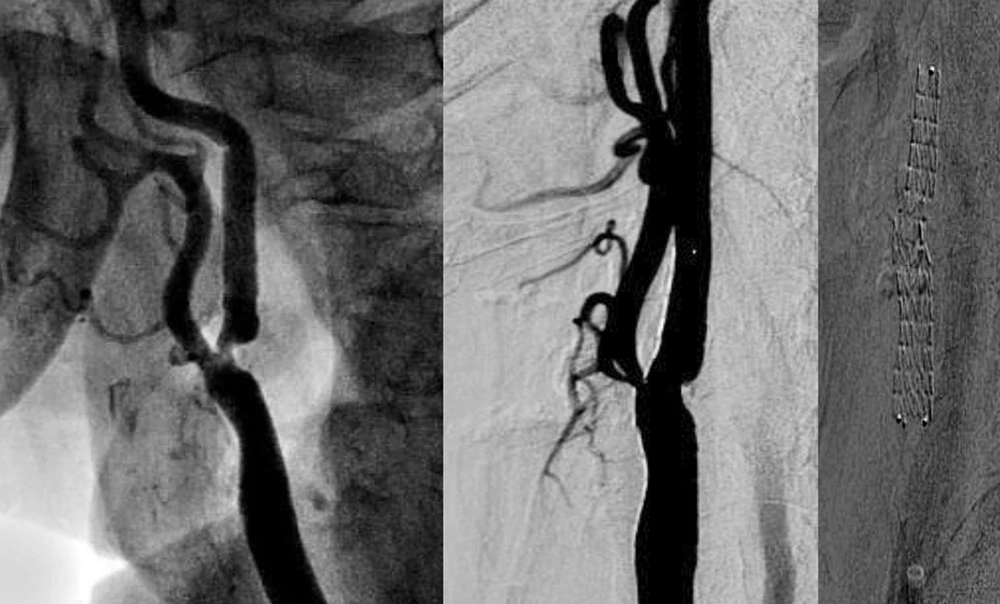
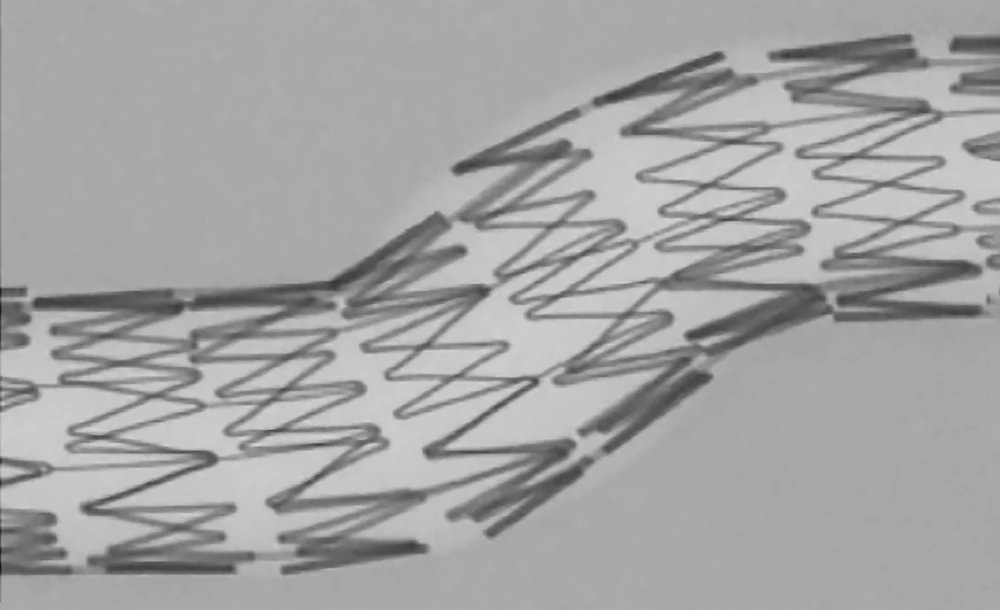
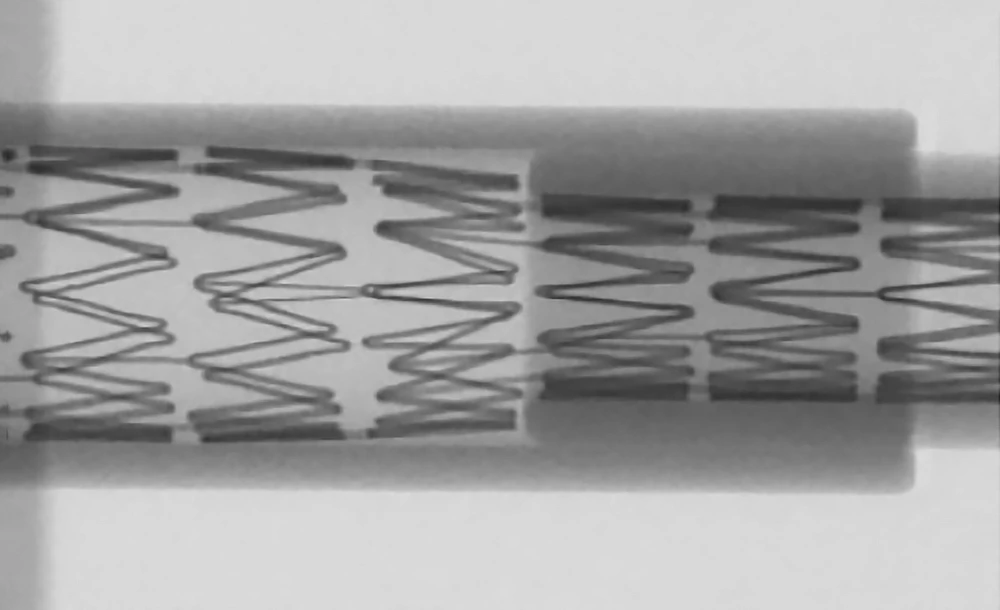
CGuard® is CE MDR Approved
The CGuard® EPS is indicated for improving carotid luminal diameter in patients at high risk for adverse events from carotid endarterectomy who require carotid revascularization and meet both criteria outlined below:
- Patients with neurological symptoms and >50% stenosis of the common or internal carotid artery by either ultrasound or angiogram or patients without neurological symptoms and >80% stenosis of the common or internal carotid artery by either ultrasound or angiogram.
- Patients having a vessel with reference diameters between 4.8 mm and 9.0 mm at the target lesion.
The following accessories are compatible with the CGuard® Embolic Prevention System:
- Proximal protective device Inner Diameter ≥2.12mm or ≥0.083" (for example 9F Mo.Ma™ ultra by Medtronic), or comparable.
- Distal protection device Emboshield™ NAV6 by Abbot Cardiovascular, or comparable.
CGuard® and the InspireMD Logo are registered trademarks of InspireMD, Inc.
Abbott® and Emboshield NAV6™ are registered trademarks of Abbott Laboratories.
Medtronic® and Mo.Ma™ are registered trademarks of Medtronic Corporation.
References:
- Musialek P et al. PARADIGM-Extend Prospective Academic Trial: Accumulating long-term evidence for MicroNet™-covered stent safety and stroke prevention efficacy. Presentation at ESC Congress 2019, Paris, France, 31 August 2019 to 4 September 2019.
- InspireMD, Inc. C-GUARDIANS Pivotal Trial: Primary Endpoint Clinical Study Report. Version F (Protocol PRO-9017).
- Yadav JS, et al. N Engl J Med. 2004 Oct;351(15):1493-1501. doi: 10.1056/ NEJMoa040127.
- Matsumura JS, et al. J Vasc Surg. 2012 Apr;55(4):968-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2011.10.120.
- Higashida R, et al. Stroke vol. 41,2 (2010): e102-9. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.564161.
- Brott TG, et al. N Engl J Med. 2010 Jul;363(1):11-23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0912321. Epub 2010 May 26.
- Kwolek CJ, et al. J Vasc Surg. 2015 Nov;62(5):1227-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2015.04.460.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Summary of safety and effectiveness data (SSED): Roadsaver/CASPER Carotid Stent System (PMA P210030). Published November 20, 2024
- Gray WA, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol Intv. 2025 Feb;18(3):367-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2024.10.031.
- Safian RD, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006 Jun;47(12):2384-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2005.12.076.
- Langhoff R, et al. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2025 Mar;Vol 48 427–37. doi:10.1007/s00270-025-04003-z.
- Wissgott C, et al. J Endovasc Ther 2017;24(1):130-137
- Musialek P, Hopkins LN, Sidiiqui AH. Postepy Kardiol Interwencyjnej