A new layer
of defense
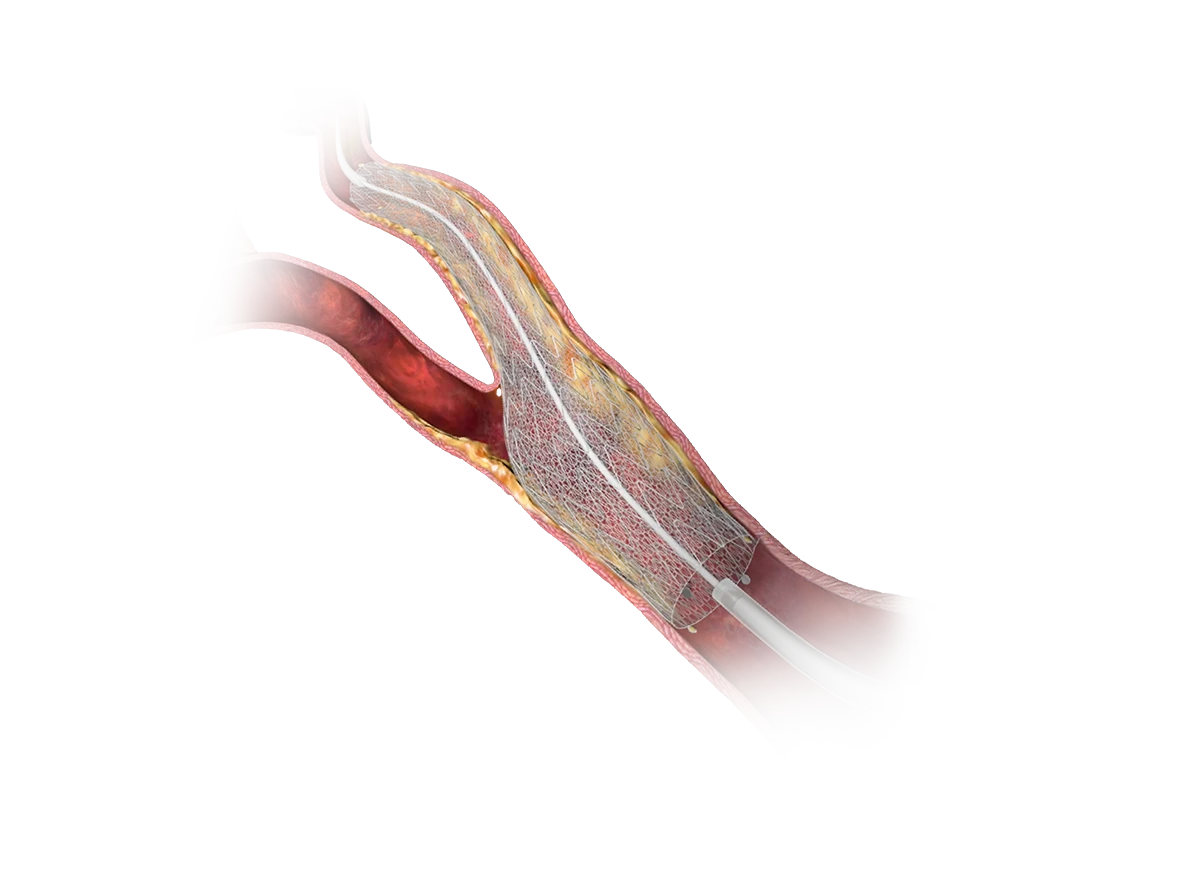


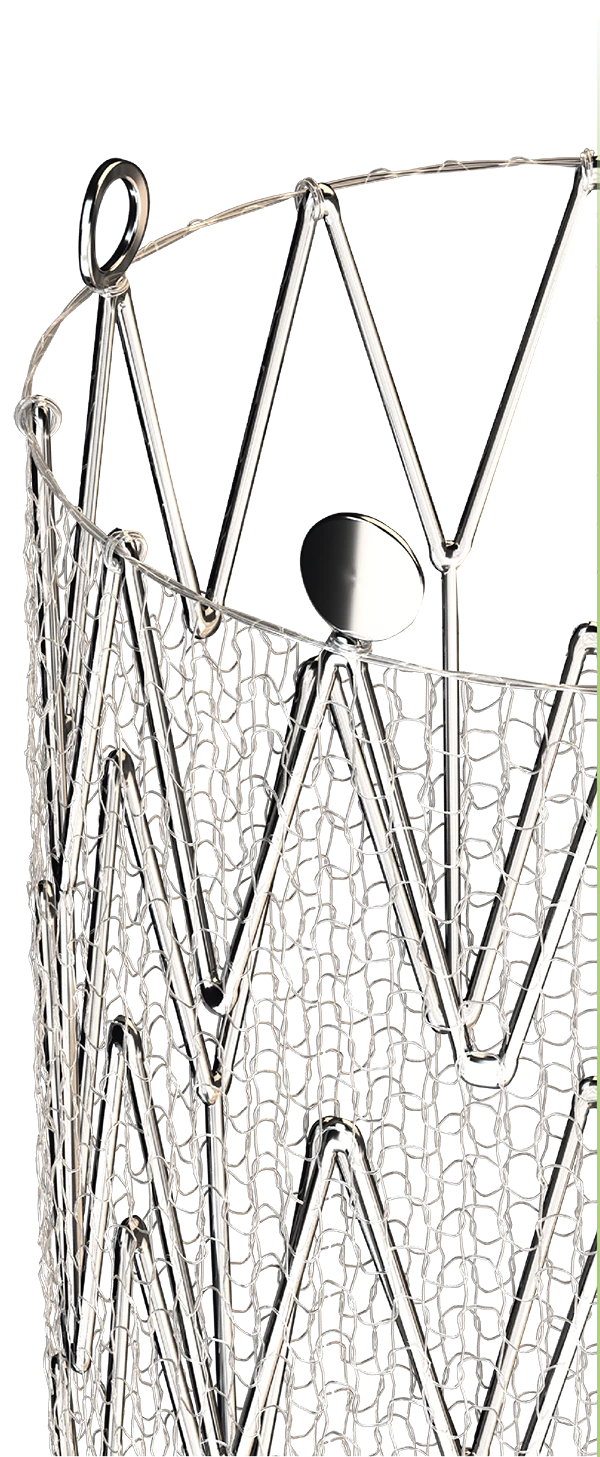
Defense designed
by InspireMD

Dual-layered, dual benefits
Expert experiences
Dr. Alberto Cremonesi
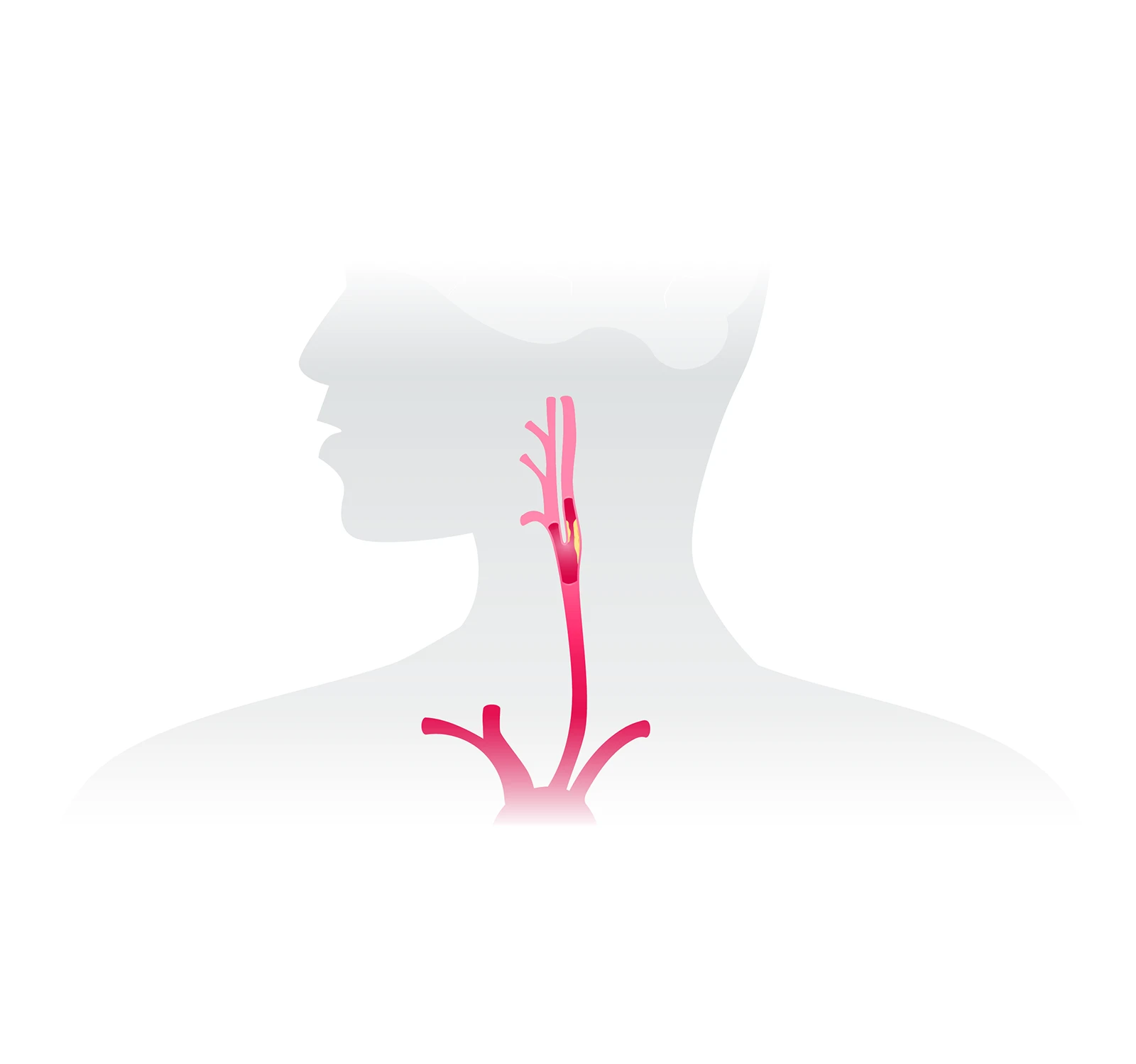
The CGuard Prime , when used in conjunction with embolic protection devices specified in the labeling, is indicated for improving carotid luminal diameter in patients at high risk for adverse events from carotid endarterectomy who require carotid revascularization and meet both criteria outlined below:
- Patients with neurological symptoms and ≥ 50% stenosis of the common or internal carotid artery by angiogram, or patients without neurological symptoms and ≥ 80% stenosis of the common or internal carotid artery by angiogram.
- Patients having a vessel with reference diameters between 6.4mm and 9.0mm at the target lesion.
The CGuard Prime should be used in conjunction with the Abbott Emboshield NAV6™ Embolic Protection System or the Medtronic Mo.Ma™ Ultra Proximal Cerebral Protection Device.
CGuard® and the InspireMD Logo are registered trademarks of InspireMD, Inc.
Abbott® and Emboshield NAV6™ are registered trademarks of Abbott Laboratories.
Medtronic® and Mo.Ma™ are registered trademarks of Medtronic Corporation.
† myocardial infarction
‡ Based on modified intent-to-treat Kaplan-Meier analysis
- World Health Organization Fact Sheet. Top 10 causes of death. 2024
- M. Bosiers, G. de Donato et al. Does Free Cell Area Influence the Outcome in Carotid Artery Stenting? European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery. Volume 33, Issue 2, 2007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejvs.2006.09.019.
- InspireMD, Inc. C-GUARDIANS Pivotal Trial: Primary Endpoint Clinical Study Report. Version F (Protocol PRO-9017).
- Yadav JS, et al. N Engl J Med. 2004 Oct;351(15):1493-1501. doi: 10.1056/ NEJMoa040127.
- Matsumura JS, et al. J Vasc Surg. 2012 Apr;55(4):968-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2011.10.120.
- Higashida R, et al. Stroke vol. 41,2 (2010): e102-9. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.564161.
- Brott TG, et al. N Engl J Med. 2010 Jul;363(1):11-23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0912321. Epub 2010 May 26.
- Kwolek CJ, et al. J Vasc Surg. 2015 Nov;62(5):1227-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2015.04.460.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Summary of safety and effectiveness data (SSED): Roadsaver/CASPER Carotid Stent System (PMA P210030). Published November 20, 2024
- Gray WA, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol Intv. 2025 Feb;18(3):367-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2024.10.031.
- Safian RD, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006 Jun;47(12):2384-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2005.12.076.
- Langhoff R, et al. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2025 Mar;Vol 48 427–37. doi: 10.1007/s00270-025-04003-z.



